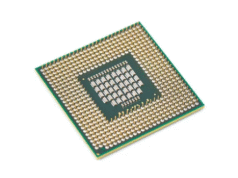
The Central Processing Unit (CPU) is often referred to as the “brain” of your computer—and for good reason. Without it, your device wouldn’t be able to perform even the most basic tasks. Whether you’re sending an email, browsing the web, or playing a video game, your CPU is working behind the scenes to make it happen. But what exactly is a CPU, and how does it work? If you’re new to tech, this guide will break it down into simple, easy-to-understand terms.
What Does a CPU Do? The Core of Every Operation
At its most basic level, a CPU carries out instructions. Think of it as the control center that takes input, processes it, and produces output. Every click you make, every letter you type, and every app you open triggers a set of instructions that the CPU must process.
In technical terms, the CPU executes a sequence of stored instructions called a program. This involves three main stages:
- Fetch – Retrieving the instruction from memory.
- Decode – Understanding what the instruction is.
- Execute – Carrying out the instruction using the computer’s resources.
These operations happen at lightning speed, often billions of times per second, which is why modern CPUs are capable of running complex applications seamlessly.
CPU Components: What’s Inside the Chip?
Even though the CPU is a small chip, it contains several vital components that allow it to function:
- Control Unit (CU): Directs the flow of data and coordinates the activities of the CPU.
- Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU): Handles all arithmetic and logic operations, such as addition, subtraction, and comparisons.
- Registers: Small memory units that store data temporarily during processing.
- Cache Memory: High-speed memory located on the CPU itself, which stores frequently accessed data for quick retrieval.
- Cores: Modern CPUs have multiple processing units called cores. Each core can process its own set of instructions, significantly improving multitasking and performance.
How Many Cores Do You Need? Dual-Core vs. Quad-Core vs. More
You may have seen terms like dual-core, quad-core, or even octa-core when shopping for a new computer or smartphone. These refer to the number of cores within a CPU.
- Dual-core: Two cores—better than single-core, allows for decent multitasking.
- Quad-core: Four cores—great for general productivity and light gaming.
- Hexa-core and beyond: Six or more cores—ideal for high-performance needs like video editing, 3D rendering, or gaming.
The more cores you have, the more tasks your CPU can handle simultaneously. However, more isn’t always better for casual users. It depends on what you plan to use your device for.
Clock Speed: Measuring CPU Performance
Another important spec is clock speed, measured in gigahertz (GHz). This determines how many cycles a CPU can perform per second. For example, a 3.5GHz CPU can perform 3.5 billion cycles per second.
Higher clock speed = faster CPU, right? Well, it’s not that simple.
A CPU with a higher clock speed might be faster, but efficiency also depends on other factors like the number of cores, thermal design, and CPU architecture. A modern CPU with a lower clock speed can outperform an older one with a higher speed due to architectural improvements.
CPU vs. GPU: What’s the Difference?
Many people confuse the CPU with the GPU (Graphics Processing Unit). While both are processors, they serve different purposes:
- CPU: Handles general tasks like running software, managing the operating system, and executing code.
- GPU: Specializes in rendering graphics and performing parallel processing, making it crucial for gaming, video editing, and machine learning.
Some computers come with integrated graphics (a GPU built into the CPU), while others feature dedicated GPUs for more intensive workloads.
Intel vs. AMD: Choosing the Right CPU Brand
The two biggest names in the CPU market are Intel and AMD. Both produce high-performance chips, but they cater to slightly different audiences.
- Intel: Known for strong single-core performance, making them great for gaming and general productivity.
- AMD (Ryzen series): Offers excellent multi-core performance and often better value for money, making them a favorite among creatives and power users.
Choosing between the two comes down to your needs and budget. Both have options ranging from budget to high-end processors.
Thermal Management: Keeping Your CPU Cool
CPUs generate heat while operating—sometimes a lot of it. That’s why cooling systems are essential.
- Air cooling: The most common method using fans and heat sinks.
- Liquid cooling: More efficient and quieter, preferred for high-performance setups.
- Thermal paste: A substance applied between the CPU and the heat sink to improve heat transfer.
If your CPU overheats, it may throttle its performance or even shut down your system to prevent damage.
Upgrading Your CPU: Is It Worth It?
If your computer is lagging, upgrading the CPU might seem like a good idea. But it’s not always that simple.
- Compatibility: CPUs must match your motherboard’s socket type and chipset.
- Cost vs. benefit: Sometimes, a new CPU requires a new motherboard and RAM too, making it more cost-effective to buy a new PC.
- Bottlenecks: If your system has other limitations (like old RAM or storage), a CPU upgrade won’t solve everything.
Still, for tech enthusiasts or gamers looking to boost performance, a CPU upgrade can be a game-changer—when done right.
Future of CPUs: What’s Next for Processing Power?
CPU technology is advancing rapidly. With the rise of AI computing, quantum processors, and ARM-based CPUs in consumer devices, the landscape is shifting.
- ARM architecture: Now used in Apple’s M1 and M2 chips, ARM CPUs are more power-efficient and offer excellent performance.
- AI integration: New CPUs are starting to include built-in AI capabilities, improving performance in smart applications.
- Smaller nodes: Manufacturers are moving to 3nm and smaller fabrication processes, which allow more transistors and better efficiency.
The future is all about smarter, faster, and greener processors.
Final Thoughts: Why Understanding the CPU Matters
The CPU might be just one part of your computer, but it plays the most crucial role in determining performance. Whether you’re buying a new device, upgrading your system, or just curious about how your computer works, knowing the basics of the CPU helps you make informed decisions.
In today’s digital world, being tech-literate is more important than ever. And it all starts with understanding what powers your device from within—the mighty Central Processing Unit.